Software Developer Success
Luck is when opportunity meets preparation
Ramping up in a new company / team
- ask questions
- pair programming or shadow experienced coworkers / ramp-up buddy
Tribal Knowledge to learn from others
- which parts are good and bad in the codebase
- which are the patterns one should follow and which ones should be avoided
- what's expected for testing and maintainability
- what's the PR process like? how many reviewers, what kind of feedback to expect?
- what's the pipeline to deployment like?
- which documentation source are reliable, and which are stale?
- introduction to partner teams and what they do
- introduction to different coworkers and when to go to them
- any other company company specific gotchas to know about
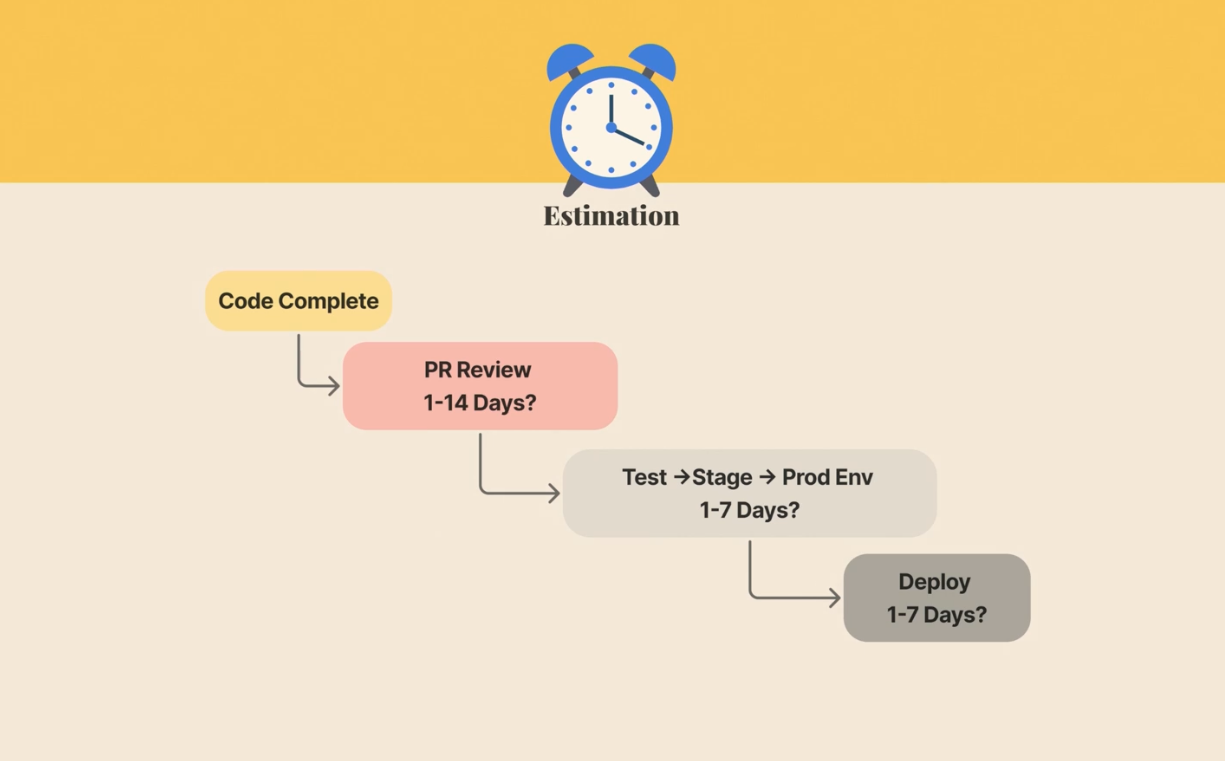
Time estimation

Estimation
-
Spike the task
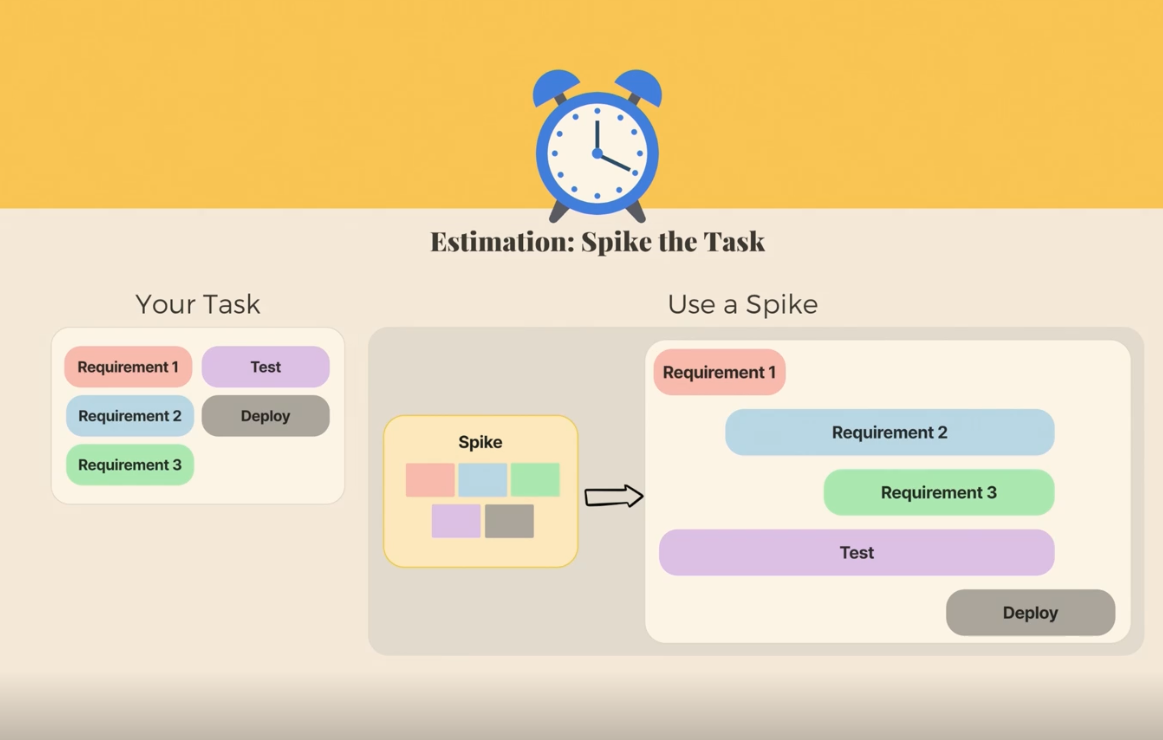
-
practice breaking down tasks and estimate how long it takes
-
understand how long it takes to get to completion in your company process
-
Over Communicate
What
- what is done
- what is in-progress
- what are blockers
- what is at risk of not being delivered
To Who
- to your manager
- to your teammates working on this task
- to any stakeholders relying on this work
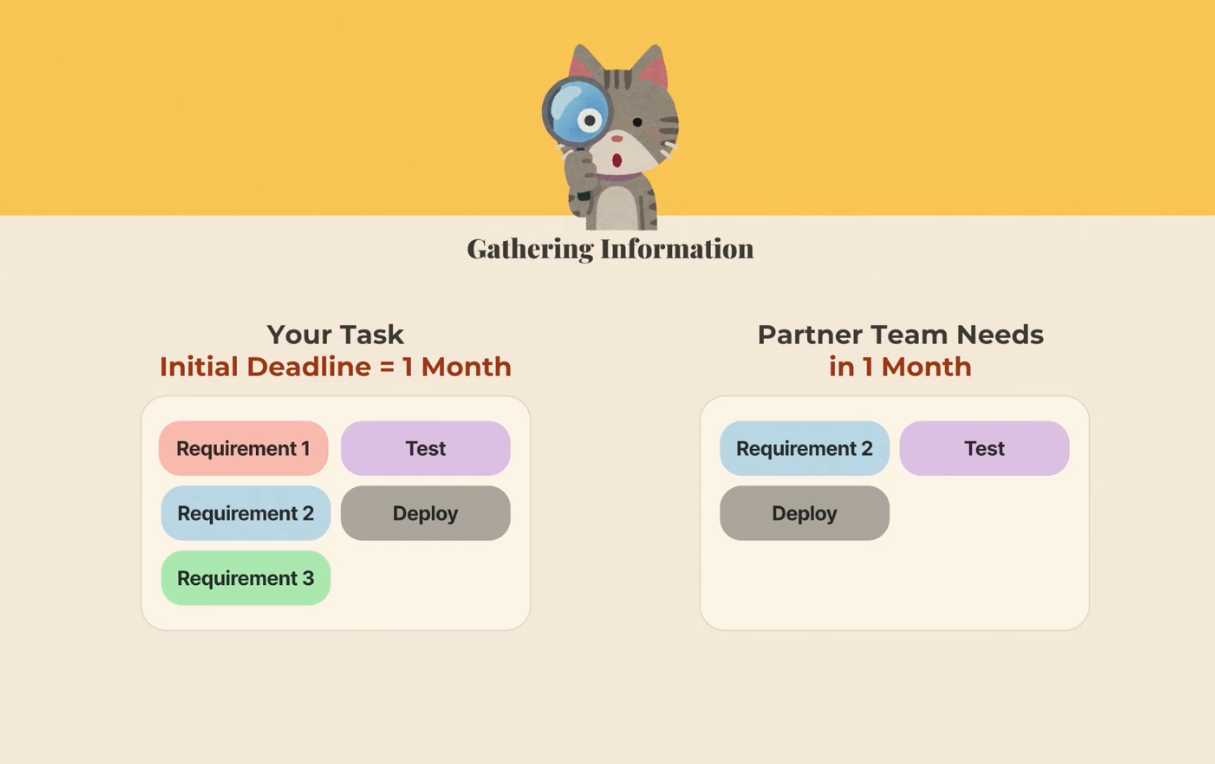
Gathering Information
- what is the tasks
- what are the validation steps
- who are the stakeholders
- who is relying on it
- why this task matters
- when is it needed
Feedback Loops
- is there something i could have done for TASK better? what areas do you think i could improve upon?
- Do you have any suggestions for how i can take on more responsibility or expand my role?
- what goals or objectives should i focus on in the upcoming months?
- how do you gain visibility into my work?
Asking for help
How?
- Time boxing
Treat each Q&A session as an opportunity to build trust:
- show your due diligence
- collaborate ona final solution
- clarify assumptions / restating the problem and solution if you are in the right course?
- express gratitude
Surfacing your accomplishments? Preparing for promotions?
-
Relying on others noticing your work is risky
-
Rewards and promotions are subjective - creating clarity and trust
-
How?
- Create and regularly update a brag doc
- Create regular communication loops with your manager
- Understand the promotion and reward process
Quality Code
- Ramp up and capture knowledge quickly
- Start delivering efficiently by understanding the codebase, company processes, and norms through shadowing and pair programming
- Focus on maintainable and testable code
- write quality code that is easy to maintain and change
- use test to understand systems and work safely
- embracing test-driven development even if it's undervalued in your company
- Overcome common blockers
- have a clear debugging process, gather information, improve estimation skills, and over-communicate to execute tasks effectively
- Seek help and prepare for growth
- be proactive in asking for help and understand steps to position yourself for promotions
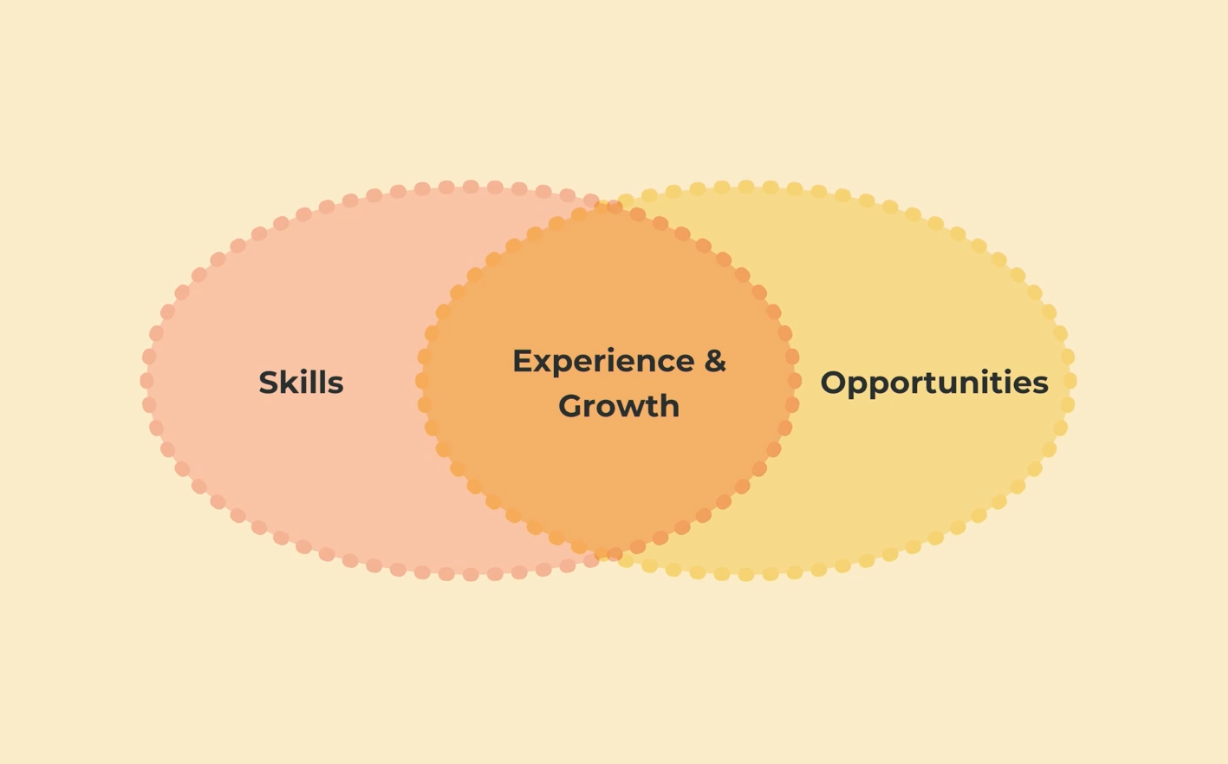

How to increase your opportunities?
-
build relationships of trust with those around you
-
you should show not tell
-
The accumulation of opportunities leads to massive growth
- Mental Trap: Good solutions speak for themselves
- Caring about other people makes you a more effective engineer
- Active listening
Guide to building relationships
- why
- mistakes and asking for help are easier when you have a relationship
- gain insights
- future job opportunities
- how
- regular face time with work-adjacent conversations
- take an interest in them and practice active listening to help you get to know them
- Sample starter questions
- how's your project going in your perspective?
- how are you feeling about RECENT_COMPANY_UPDATE
Active listening
- no judgement, no shame, no blame


What is considered quality code?
- maintainable, stable, and easy to change
- simple and straight forward
- not perfect, but delivers the company's needs
Clean code basics
- use descriptive naming
- write decoupled code
- follow the single responsibility principle. Each function has a single responsibility
- have a clear organization of code both in the folder hierarchy and in individual files.
- Lean into colocation for project structure. (Things that change together should stay together)
- use comments appropriately: comments should describe why, not what and how. Your code should be descriptive on its own.
- avoid code duplication
- add test coverage and write good test
Test Driven Development
Steps
- Identify the feature or condition needed in your code
- Write a failing test case for the desired behavior.
- Write code to pass the test in the simplest and brute force way possible
- Run the test to ensure it passes and produces the expected output
- Repeat the process for each new feature or condition needed. Ensure previous cases doesn't fail with new changes
- Look for opportunities to refactor or improve the code.
Refactoring techniques
- When working existing code , add (if it doesn't exist) a test suite to:
- understand it
- safely refactor it
- document its behavior for future developers
- Create a 'seam' to safely inject new code in an existing codebase
- refactor code in iterations
Why TDD & Tips for learning
- Changing code is safe: with tests, you can easily refactor or change the code without worrying you are breaking existing functionality or making unintended impacts
- Simpler solutions: Leads to simpler and less complex code solutions because you aren't over-thinking the solution
- Easier to solve: Allows you to focus on solving one small chunk at a time, making the problem easier to solve
- Less bugs: Writing and testing code one piece at a time is less error-prone
Tests in the industry
- it is considered a best practice, but not a lot of companies and teams actually do it
- Plagued by common pitfalls:
- done as an after thought
- testing the wrong things (implementation details), which does not provide useful signals and makes its painful to maintain which leads to developers not looking at or writing tests.
Working with existing code
- use the debugger to understand the relationship between code modules(breakpoint, scope, call stacks)
Debugging
- walk through the code step by step, checking assumptions and outputs
- use console.log statements
- utilize the debugger to understand the code state and execution flow
- try isolating the issue by commenting out code until the problem is identified.
- consider talking through the problem which a person, pet, rubber duck, and etc.
Resources
https://frontendmasters.com/courses/dev-soft-skills/working-with-existing-code/